⸺Degenerative diseases⸺
The cervical spine
Spinal canal stenosis, osteoarthritis, osteochondrosis, myelopathy
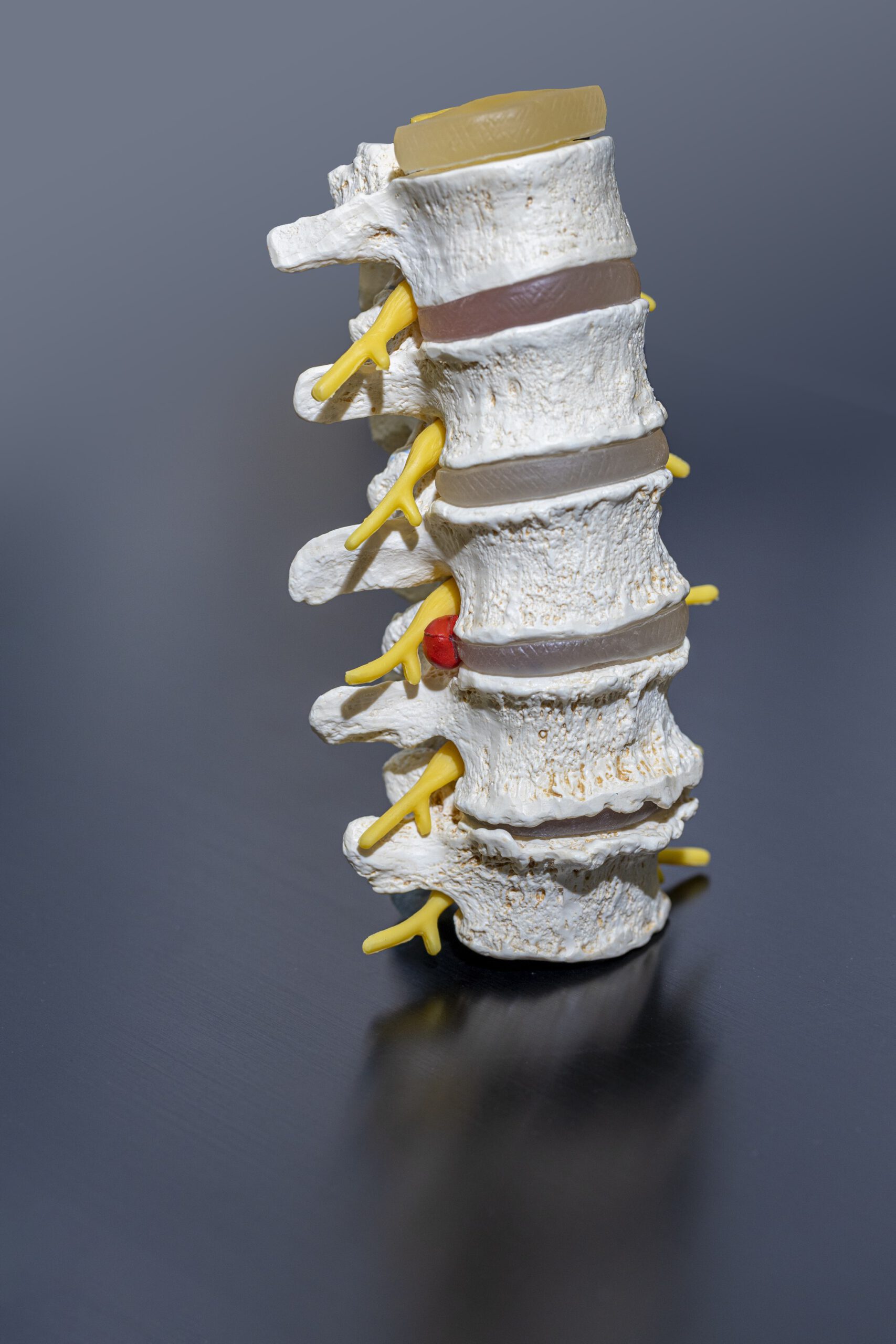
Age-related wear and tear on the joints, ligaments, muscles and weight-bearing elements can lead to degenerative diseases of the cervical spine. Advanced wear and tear of joints leads to spondylarthrosis, osteoarthritis of the small joints.
The degeneration of the discs and intervertebral spaces can lead to herniated discs, but also to the so-called osteochondrosis. This is a wear-related change of the disc and the adjacent vertebrae. Constant overload causes the discs in the spine to be compressed and cannot regenerate over time. Wear processes on the cervical spine can constrict the neural structures such as the spinal cord and nerve roots. It is called spinal stenosis.
Cervical myelopathy is a disease usually caused by wear and tear. It mainly occurs in older age and is often due to pre-disposition. Pressure on the spinal cord causes damage. Symptoms manifest as neck pain, numbness or disturbance of sensation in the upper extremities, and deficits in gross and fine strength and sensitivity. Gait disorders or disorders of the bladder or bladder Rectum disorders occur at an advanced stage.
Often the advanced wear leads not only to a narrowing of neural structures, but also to a curvature of the cervical spine and thus to further loads on vertebrae, musculature, ligaments and discs.
Konservative Behandlung
Meistens können die Beschwerden erfolgreich ohne Operation behandelt werden. Dabei kommen physiotherapeutische, physikalische und Manual therapeutische Maßnahmen sowie begleitende medikamentöse Therapien zum Einsatz. Häufig hilft Patienten mit Rückenschmerzen schon eine Gewichtsabnahme sowie ein muskulärer Aufbau. In fortgeschrittenem Stadium können gezielte Infiltrationen, in die kleinen Gelenke der Wirbelsäule (sog. Facetten-Infiltration) oder in die Nähe der Nervenwurzeln (sog. PRT/ Periradikuläre Infiltration) die Beschwerden lindern.
Operative Therapie
Wenn die konservative Behandlung keine Linderung bringt oder die Einengung der Nerven zu Funktionsausfällen führt oder dies bei unbehandeltem Verlauf zu erwarten ist, wird sich der behandelnde Arzt für eine Operation entscheiden. Moderne Techniken, deren Einsatz individuell auf den Patienten abgestimmt werden, und ein hoher Behandlungsstandard ermöglichen operativen Eingriffe mittlerweile auch bei Patienten im hohen Alter.
⸺Degenerative diseases⸺
The cervical spine
Spinal canal stenosis, osteoarthritis, osteochondrosis, myelopathy
Age-related wear and tear on the joints, ligaments, muscles and weight-bearing elements can lead to degenerative diseases of the cervical spine. Advanced wear and tear of joints leads to spondylarthrosis, osteoarthritis of the small joints.
The degeneration of the discs and intervertebral spaces can lead to herniated discs, but also to the so-called osteochondrosis. This is a wear-related change of the disc and the adjacent vertebrae. Constant overload causes the discs in the spine to be compressed and cannot regenerate over time. Wear processes on the cervical spine can constrict the neural structures such as the spinal cord and nerve roots. It is called spinal stenosis. Cervical myelopathy is a disease usually caused by wear and tear. It mainly occurs in older age and is often due to pre-disposition. Pressure on the spinal cord causes damage. Symptoms manifest as neck pain, numbness or disturbance of sensation in the upper extremities, and deficits in gross and fine strength and sensitivity. Gait disorders or disorders of the bladder or bladder Rectum disorders occur at an advanced stage. Often the advanced wear leads not only to a narrowing of neural structures, but also to a curvature of the cervical spine and thus to further loads on vertebrae, musculature, ligaments and discs.
Conservative treatment
Most of the time, the symptoms can be treated successfully without surgery. Physiotherapy, physical and manual therapy and drug therapies are used. Targeted injections, called infiltrations, into the small joints of the spine or near the nerve roots, can also relieve the symptoms.
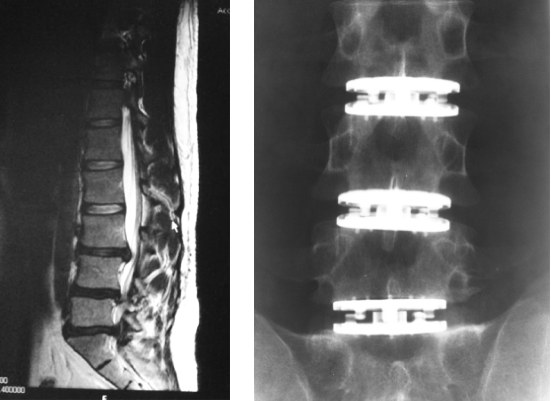
Surgical treatment
If the conservative treatment does not bring relief, or the narrowing of the nerves leads to loss of function, or if this is to be expected if left untreated, the attending physician will opt for surgery. Modern techniques, whose use is individually tailored to the patient, and a high standard of care allow surgical interventions even in elderly patients.
